Table of Contents
What is Change Management?
Change management is a structured approach to implementing and managing organizational change.
It refers to the actions taken by the management to transition the entire organization to accept and embrace this change.
Understanding change management is important because no business exists in stagnation. Business, by nature, is dynamic, and change management helps business stakeholders adapt to the constantly changing landscape.
Importance of Change Management
Change is the only constant – this is especially true for businesses. Change management is important in order to ensure that these unavoidable changes are implemented smoothly and with minimal disruption.
Change management enables organizations to adapt quickly and effectively to evolving market conditions, technological advancements, and competitive landscapes.
With change management, there is reduced resistance to change. Change management fosters employee acceptance by actively involving employees in the change process, addressing their concerns, and providing clear communication.
This improves the chances of the change being successfully implemented. Change management addresses the needs of all business stakeholders – employees, customers, suppliers, partners and investors, thus improving stakeholder buy-in.
Steps in Change Management
Effectively managing change requires a systematic approach that involves a series of steps. Here are the steps in change management:
Assess the Need for Change
The first step in change management is to define the need for change by thoroughly assessing the situation. Internal and external factors must both be analyzed for areas of improvement.
For example, the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic required businesses to create infrastructure to support employees working from home and cost-cutting measures to retain liquidity in a time of economic difficulty.
Vision for Change
Once the need for change is properly defined, the HR team can develop a plan to implement these changes.
The plan must be realistic and defined regarding measurable Key Performance Indicators and metrics. Project stakeholders and a team must be constituted to oversee the change, and the term and scope must also be properly defined.
While this structure is important, providing flexibility and accounting for unknown variables is also important.
Introduce Changes within Organization
Implementing the plan and sticking to deadlines is the most important part of change management. HR managers in charge of implementing this change will have to keep a close eye on the pulse of the organization – communication and feedback is key to ensuring successful adaption of change.
Review Progress & Analyse Results
Post plan implementation, it is important to review the change initiative in order to understand how successful or unsuccessful the plan was.
The learnings from this analysis will help with future plans and projects.
How to Implement Change Successfully
Organizations can use one or a combination of the many change management models to implement change successfully.
A change management model is a framework that helps organizations navigate change initiatives and achieve goals.
There are a number of different change models theorized by behavioural and social psychologists.
Change Management Models
ADKAR’s Change Management Model
The ADKAR model of change management was created by Jeffrey Hiatt, the founder of Prosci, a company dedicated to change management.
ADKAR stands for:
Awareness of the need for change
Desire to participate and support the change
Knowledge of how to change
Ability to implement desired skills & behaviours
Reinforcement to sustain the change
The ADKAR model focuses on change at the individual level. It helps identify areas of resistance. For example, a person might have the awareness of the need to change, but might not want to change – the lack of desire to change could be the point of resistance.
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
John Kotter is a professor at Harvard Business School and a change expert. His 8-step model of change helps organizations anchor their change management projects around a structured framework.
Step 1: Create a sense of urgency
Step 2: Build teams to guide the workforce
Step 3: Develop a vision and strategy
Step 4: Communicate the vision
Step 5: Empower employees to take action
Step 6: Create short-term wins
Step 7: Analyse individual successes and improvements
Step 8: Sustain and maintain changes
Nudge Theory
 Nudge theory is a concept in behavioural psychology – it proposes that subtle changes in choice architecture can nudge people towards making better decisions for themselves and society.
Nudge theory is a concept in behavioural psychology – it proposes that subtle changes in choice architecture can nudge people towards making better decisions for themselves and society.
Nudge theory can be a non-intrusive, cost-effective way to influence employee behaviour and decision-making. Reward systems and subtle design changes go a long way in getting employees to cooperate and embrace change.
For example, organizations can incorporate nudges to promote employee participation in training and development programs. Providing personalized recommendations or incorporating gamification elements can increase engagement and skill development.
Lewin’s Change Management Model
Kurt Lewin, one of the great pioneers of modern psychology, created the 3-stage change management model.
The model consists of three stages:
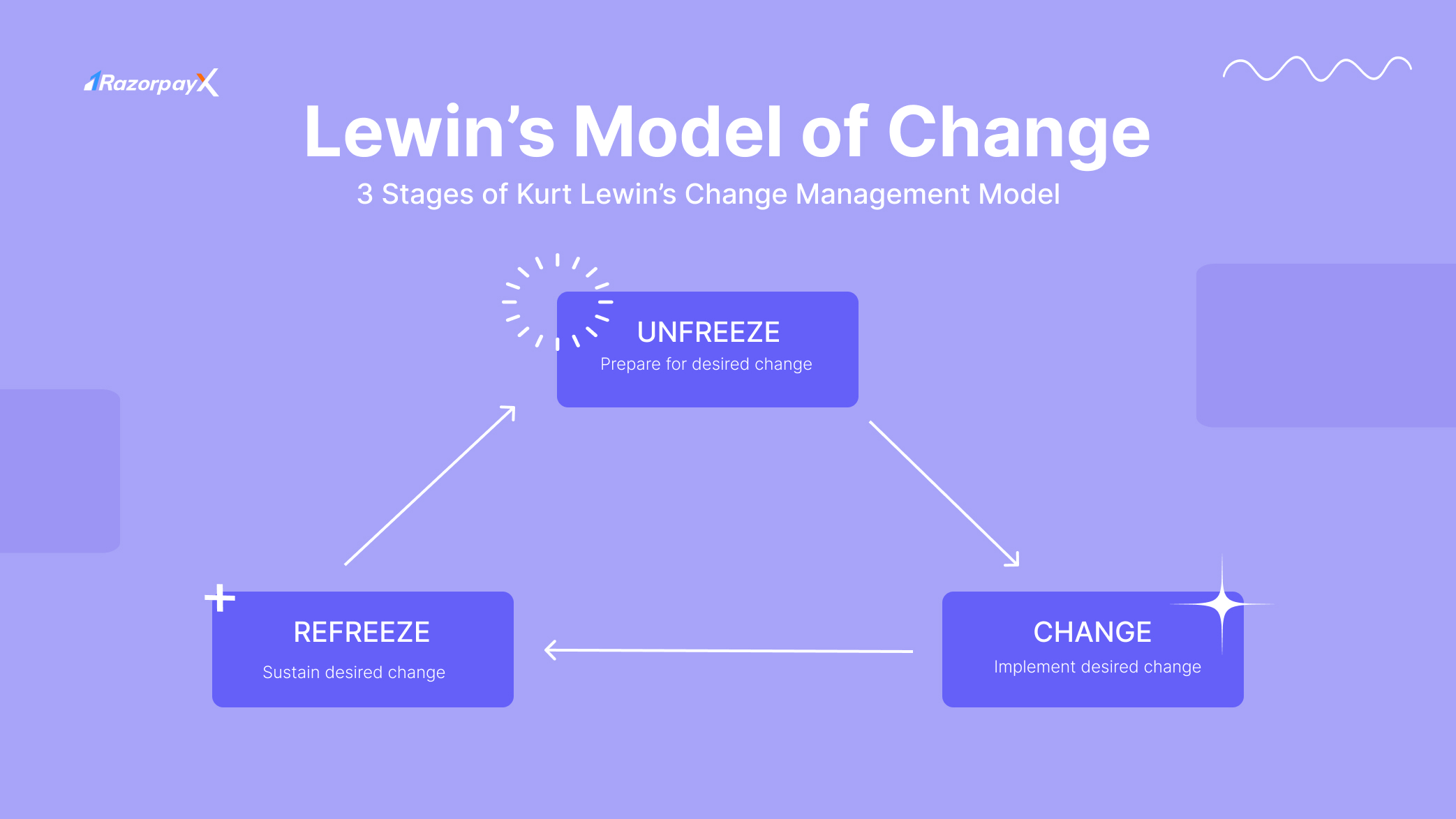 Unfreezing: This stage involves assessing the need for change, identifying the driving forces and restraining forces for change, and creating a sense of urgency. It also involves communicating the need for change to all stakeholders and building a strong coalition of support for the change initiative.
Unfreezing: This stage involves assessing the need for change, identifying the driving forces and restraining forces for change, and creating a sense of urgency. It also involves communicating the need for change to all stakeholders and building a strong coalition of support for the change initiative.
Changing: This stage involves developing a detailed change plan that outlines the specific steps, timelines, resources, and responsibilities for implementing the change. It also involves providing training and support to employees, addressing resistance to change, and monitoring progress.
Refreezing: This stage involves reinforcing the new behaviors and processes, making them the new norm, and preventing the organization from reverting to its old ways. It also involves celebrating successes and recognizing the contributions of employees who helped to make the change successful.
McKinsey 7-S Model
The McKinsey 7S Model is a framework for understanding and managing organizational change. It identifies seven key elements that must be aligned for successful change:
-
Structure: The organization’s structure, or how it is organized, should be aligned with the desired change. This may involve changes to reporting relationships, job roles, or processes.
-
Strategy: The organization’s strategy, or its long-term plan for achieving its goals, should be aligned with the desired change. This may involve changes to the organization’s products, services, or markets.
-
Systems: The organization’s systems, processes, and procedures should be aligned with the desired change. This may involve changes to the organization’s IT, HR, or financial systems.
-
Shared Values: The organization’s shared values, or core beliefs and principles, should align with the desired change. This may involve changes to the organization’s mission statement, values statement, or code of conduct.
-
Skills: The organization’s skills, or the abilities of its employees, should be aligned with the desired change. This may involve training and development programs, recruitment of new employees, or changes to performance management systems.
-
Style: The organization’s style, or its leadership and management approach, should be aligned with the desired change. This may involve changes to the organization’s culture, decision-making processes, or communication style.
-
Staff: The organization’s staff or employees should be aligned with the desired change. This may involve changes to the organization’s hiring practices, employee engagement initiatives, or rewards and recognition programs.
Types of Organizational Change
Organizational change can be broadly classified into five types:
Strategic change
When there is a fundamental change in the organization’s strategy, goals or structure, it can cause disruption to the workplace culture and employee attitudes. Strategic change is done to keep the business profitable and healthy in times of change to the market, the introduction of disruptive technology or competition.
Examples of strategic change include mergers and acquisitions, divestitures, new product launches and changes to business models.
Structural change
Strategic change usually results in changes to the organization’s reporting structure and hierarchy. It is implemented by way of reorganizations or layoffs.
This kind of change can be alarming to employees – there could be fears of being laid off or moved to different departments. Change management is important to manage structural change and keep employee morale up.
Operational Change
Another consequence of strategic change is operational change; this includes updating business processes or streamlining systems to meet certain goals.
Operational change can be challenging to manage due to potential disruptions to existing processes and the need for employee buy-in.
Successful operational change can bring significant benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Cultural change
This type of change involves changes to an organization’s culture, values, or employee behaviour. It is often driven by a need to keep up with the changing cultural landscape that the company operates in or to improve employee engagement or productivity.
Examples of people-centric change include leadership training, diversity and inclusion initiatives, and changes to performance management systems.
This type of change involves the adoption of new technologies or the modification of existing technologies.
Innovation keeps business processes efficient and productivity at its maximum – this is why technological change is among the most important in any organization.
Examples of technological change include the implementation of new software, the adoption of AI-enabled tools, and the adoption of cloud computing.
Unplanned change
This type of change is not planned or anticipated. It can be caused by various factors, such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or changes in government regulations. Unplanned change can be disruptive and difficult to manage, but it can also allow organizations to adapt and innovate.
For example, the COVID-19 pandemic caused huge disruptions to the supply chain – businesses worldwide had to quickly adapt and implement operational changes to stay afloat.
Change Management & HR
In most organizations, change management is a function of the HR department.
The HR department has a number of other functions, including payroll, employee engagement and management, and so much more.
As a result of this stretched bandwidth, change management is not given the importance it deserves in most businesses.
One way to improve business focus on change management is to automate other HR functions like payroll or compliance.
RazorpayX Payroll is India’s only fully automated payroll & HR software. With features like auto-filing & payment of compliances like PT, PF, TDS and ESIC, businesses can focus resources on strategic work like change management.
FAQs
What is change management?
Change management is a structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organisations from a current state to a desired future state. It encompasses a range of activities, from defining the change and assessing its impact to communicating the change and providing support to those affected by it.
What are some common challenges to change management?
Common challenges to change management include resistance to change, lack of communication & transparency, unrealistic expectations and inadequate resources.
What are some tools and techniques for change management?
Tools for change management include change management software to track progress and manage tasks; change champions who can advocate for the change within the workplace and help build support; videos, guides and brochures for employees to refer and read.
Why is change management needed?
Change management is needed to help organizations effectively navigate change, reduce resistance, increase employee engagement, and improve the likelihood of successful implementation.





