Margin Calculator
Loading Margin Calculator…
Check Razorpay products for your business
Razorpay POS
Collect payments swiftly in your store with Razorpay POS and its interesting offers.
Payment Pages
Easiest way to accept international and domestic payments with custom-branded online store.
How to use margin calculator
- Fill in the Cost Price (CP), Selling Price (SP), and any Additional Costs like packaging or shipping.
- The calculator automatically shows your Profit Amount, Profit Margin %, and Markup % along with a visual chart.
- Download a detailed report (PDF), email the results, or share directly via WhatsApp.
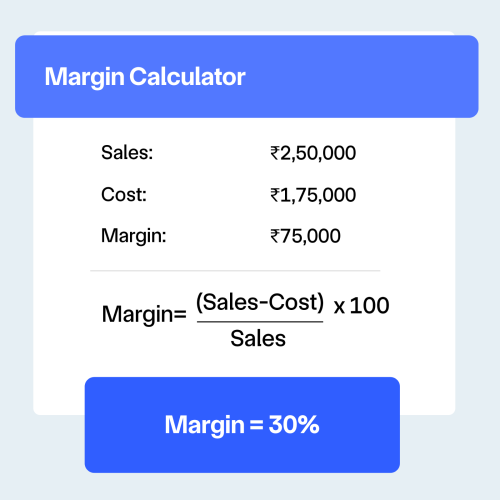
Maximize profits with gross margin management
- Track how much revenue remains after covering costs to identify winning products.
- Adjust pricing and reduce expenses to increase retained earnings efficiently
- Higher margins provide resources to reinvest, scale operations, and grow faster.
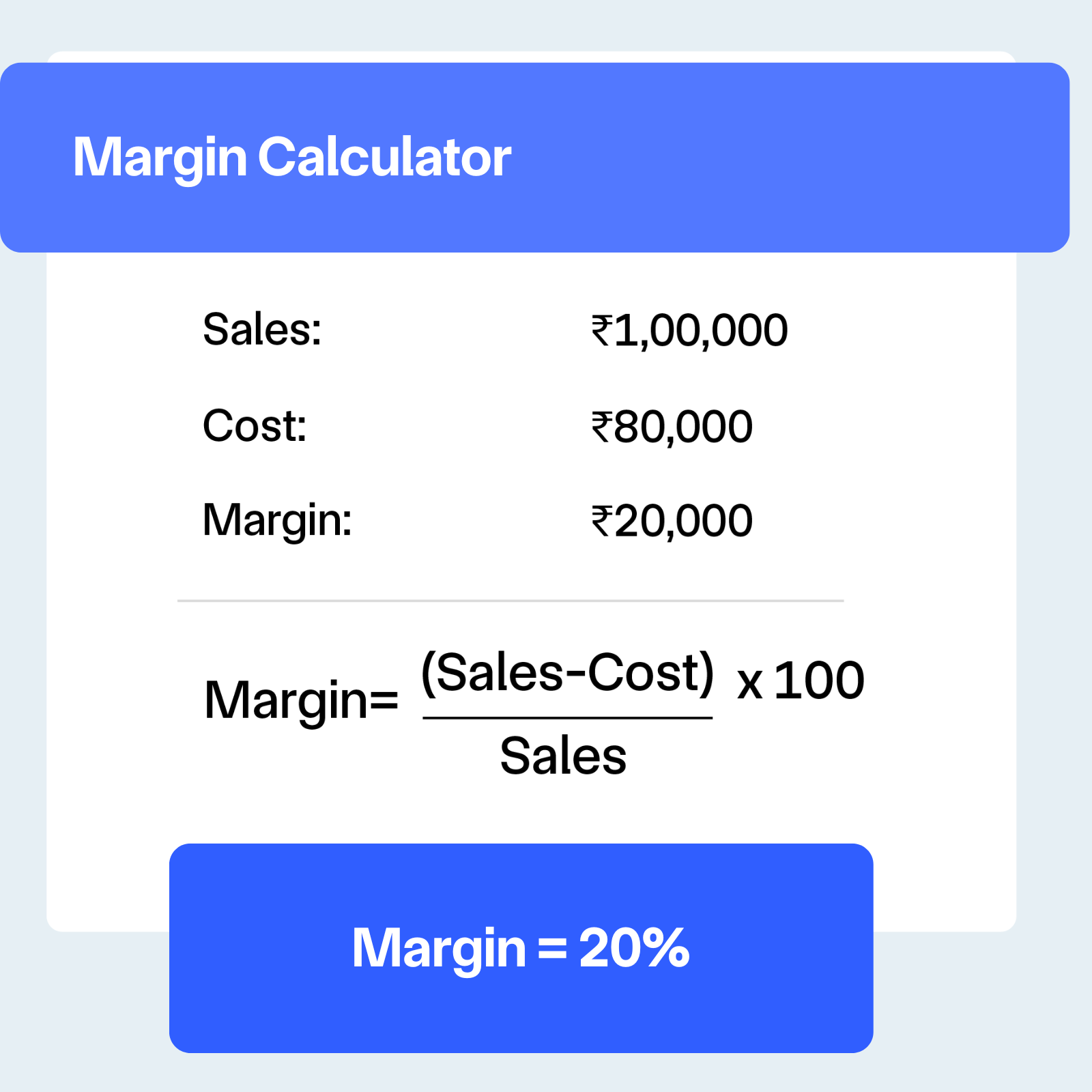
Gross margin formula
- Gross Margin Formula – Gross Margin % = ((Selling Price – Cost Price) / Selling Price) × 100
- Example (in INR) – If you sell a product for ₹100 and it costs ₹60 to produce: Gross Margin = ((₹100 – ₹60) / ₹100) × 100 = 40%. This means you retain 40% of your selling price as gross profit.
- Alternative Methods – Gross Margin = (Gross Profit / Revenue) × 100; and Gross Profit = Selling Price – Cost of Goods Sold.
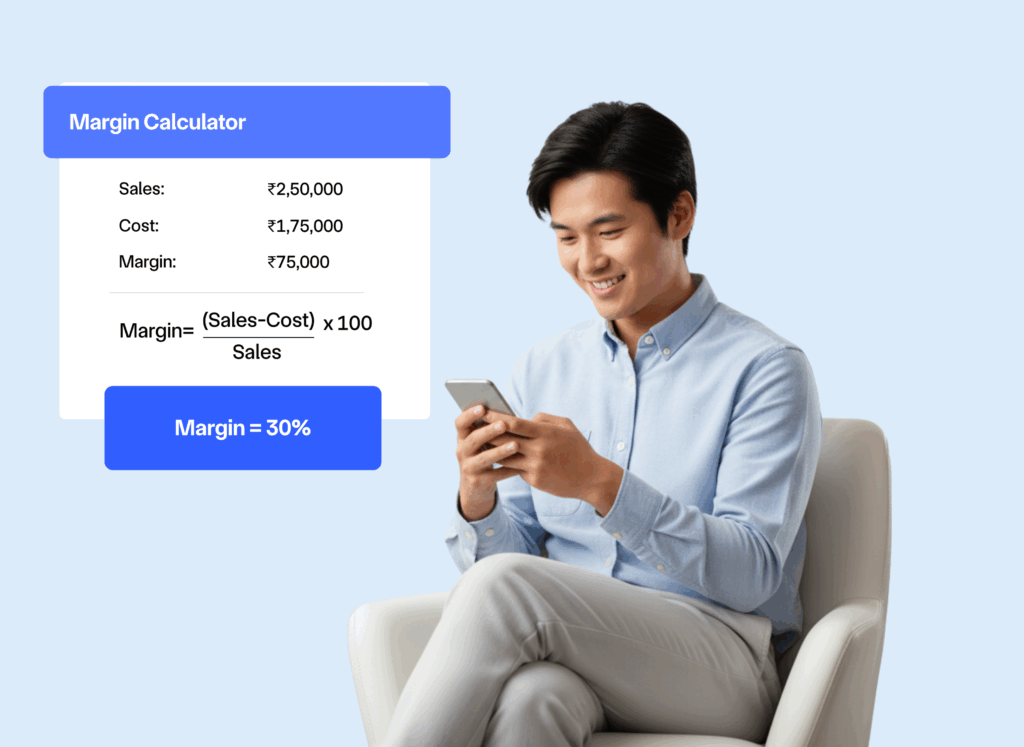
Factors affect business margins
Industry standards
Play a significant role, as different sectors have varying typical margin ranges. Technology companies often enjoy higher margins than retail businesses due to different cost structures.
Competition level
Directly impacts pricing power. Highly competitive markets typically compress margins, while unique or innovative products may command premium pricing.
Operational efficiency
Affects costs and subsequently margins. Streamlined operations, bulk purchasing, and optimized supply chains can improve profitability.
Product mix
Influences overall margins, as different products or services may have varying profitability levels. Focusing on higher-margin offerings can boost overall performance.
Scale and volume
Often improve margins through economies of scale, better supplier negotiations, and fixed cost distribution across larger volumes.
Economic conditions
Impact both costs and customer willingness to pay premium prices. Inflation, supply chain disruptions, and market demand fluctuations all affect margins.
What is a good profit margin?
- Industry Benchmarks provide context for evaluation. Software companies might target 70-80% gross margins, while grocery stores typically operate on 2-3% net margins
- Gross margins above 50% are strong, and net margins above 10% indicate healthy profitability. Service businesses typically achieve higher margins than product-based ones.
- Tracking margins over time reveals important signals. Improving margins reflect growing efficiency or market strength, while declining margins point to competition or inefficiencies.
Use cases for margin calculation
Retailers & wholesalers
Set selling prices that stay competitive while ensuring consistent profit margins.
Startups
Test and evaluate different pricing models during early-stage business planning to make informed decisions
Manufacturers
Analyze product-level profitability by factoring in raw material, labor, and additional production costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I calculate profit margin percentage?
Profit margin percentage = (Revenue – Costs) ÷ Revenue × 100. A margin calculator makes this quick and error-free for both single products and overall business analysis.
What’s the difference between margin and markup?
Margin is profit shown as a percentage of selling price, while markup is profit shown as a percentage of cost price. Both are used in pricing strategies but reflect different perspectives.
Can I use the calculator for multiple products?
Yes. Most margin calculators allow you to analyze products individually. For a portfolio of items, use weighted averages to calculate overall margins.
How often should I review my margins?
It’s best to review margins monthly for operational insights and quarterly for strategic planning. Regular checks help you spot trends and react quickly.
What if my margins are below industry standards?
Below-average margins suggest you may need to adjust pricing, cut costs, or improve efficiency. A calculator helps you model different scenarios for improvement.
Can the margin calculator show both gross and net margins?
Yes. Many calculators provide gross margin (focused on direct costs) and net margin (after all expenses), giving you a clearer picture of profitability.
Is there an ideal margin percentage for all businesses?
No single benchmark applies to all. Tech and SaaS firms may achieve 70–80% gross margins, while retail businesses often operate on single-digit net margins
Can I use a margin calculator to set selling prices?
Yes. By entering your cost and desired margin percentage, the calculator can work backwards to suggest an optimal selling price that meets your profitability target