Introduction
Technical writing has been essential in documenting various technical processes that effectively communicate with ordinary people, be it a guide to assembling a simple table or easy integration of complex software.
Today, it is crucial to ensure that whatever you put on the internet is visible to your targeted users. The same applies to technical writing. The step-by-step approach might have made it easy for a user to comprehend the technical data, but the real question is- “Is it easy for them to reach your piece of documentation?”
There are a bunch of things you can do to kick-start your visibility journey:
- Set up visibility metrics for your documentation website
- Integrate analytics to get better data
- Know the difference: Organic vs. Paid
There is, however, one masterstroke that enhances your website visibility, whether through organic or paid techniques – Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a methodology that involves the optimisation of the website in order to increase its visibility in Search Engines Result Pages (SERPs) and gain qualitative and quantitative traffic. The increased traffic further leads to improvement in conversion rates, i.e., no. of visitors that get converted to potential customers. Through search engine bots, the websites undergo processes like crawling, indexing, and ranking. Shortcomings in any of the functions might lead to a lack of visibility in search engines.
Before dwelling deeper into the functionality of SEO, let us give you a small example: If you search for, say, “Restaurants” in Google, the websites that appear on the result page are much different than that of “ Restaurants in Mumbai” or “Vegetarian restaurants in Mumbai”. Adding keywords like “Mumbai” or “Vegetarian” filters out many websites, thus improving their visibility on the result pages.
Organic or Paid
The search results can either be Organic or Paid. Organic results are driven by user traffic, quality content, and optimised website metrics.
In contrast, paid results are often sponsored like the pay-per-click model by Google Ads.
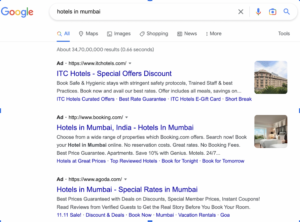 In the above example, the search engine follows an algorithm based on different factors to order and rank result pages. And you can make use of this algorithm and implement SEOs through the following techniques:
In the above example, the search engine follows an algorithm based on different factors to order and rank result pages. And you can make use of this algorithm and implement SEOs through the following techniques:
- Using the right and distinct keywords
- Creating high-quality content
- Improving the website user-interface
- Working on metrics like loading speed, loading time, stability, etc.
- Understanding the importance of URLs, tags, and links
All of these techniques can be implemented by three different approaches.
- White hat SEO – SEO implementation that follows Google’s guidelines for better user experience.
- Black hat SEO – Using unethical practices and manipulating Google’s algorithm to rank higher in SERPs.
- Grey Hat SEO – A combination of both black & white hat SEO.
However, we recommend you go for the most legal and regulated way- White hat SEO.
Types of SEO
Common types of SEO:
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
- Technical SEO
On-page SEO
This particular type concerns SEO activity carried out directly on the website or webpage. Ticking the boxes on certain on-page ranking factors can be of great help if you are looking to implement on-page SEO. A few of them are listed below:
- Optimised URLs: Your URLs are often the first thing a user sees when trying to search for something. Keep your URLs short, crisp and human-readable. URL Example:
Good: https://razorpay.com/payment-gateway/
Bad: https://razorpay.com/1232payment-gateway/70sign_ref_c
Also, add some common keywords or key phrases that are often searched for into the URLs and the page content to improve visibility. Some popular keyword research tools are SEMrush, Google keyword planner, Keyword surfer, etc.
- Content structuring: To improve user readability, you can work on how you structure your content. You can divide the content into specific sections adorned with proper headings and subheadings to create a concise segmentation and a hierarchy.
- Relevant visuals: Long paragraphs of documentation can often be monotonous. You can add visuals in the form of GIFs and infographics to keep your users stuck to the screen while going through your content. Add ALT tags ( text description) to each image to help elevate ranking during image searches.
- Defined titles and Meta descriptions: Add defined title tags to your website so search engines can understand your documentation’s intent and push it to maximise user clicks. The same goes for meta tags and meta descriptions– targeted keywords, to-the-point descriptions, and appropriate lengths.
- Keyword cannibalization: Avoid using the same keywords, duplicate titles, and descriptions on different pages of your website.
 This reduces the crawling, leading to less traffic and lower ranking. You can either replace these keywords or combine them into one comprehensive document.
This reduces the crawling, leading to less traffic and lower ranking. You can either replace these keywords or combine them into one comprehensive document. - Duplicate content: If you are working on different versions of pages in your website, in particular, you can work on making each version distinct through canonical tags, redirecting links, or simply rewriting the duplicate content to prevent the indexing of multiple pages instead of the main webpage.
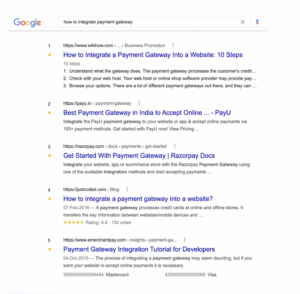
For example, you can see the SERP of “How to integrate a payment gateway” based on keyword rankings, URL optimisation, Optimised meta tags, etc.
Off-page SEO
As the name suggests, off-page SEO refers to the SEO activities carried out through other sources instead of your own webpage. It can be through blogs/articles, ads, social media, content marketing, etc. Either way, the goal is to drive the rankings through the ceiling.
The most common form of achieving off-page SEO is through external blogs or resources. Adding backlinks to your own website works as a charm in gaining some organic traffic from different websites.
You can also attract paid traffic by posting sponsored ads on various social media channels. This sometimes helps pull in a lot of users based on their web activity.
Technical SEO
You must know there is more to SEO than your website’s content. Website functionality is equally important. Technical SEO touches on some core aspects of technical writing, hence the most popularly used type of SEO for technical writers.
Let’s highlight things to consider while working with technical SEO.
- Secure connection: Use HTTPS to encrypt the connection between the browser and the site. It will prevent private data from being intercepted, warranting privacy & security.
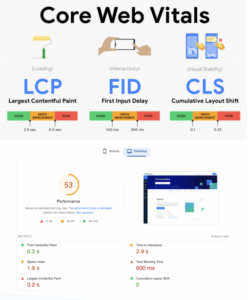
- Website user interface: Try to make your website’s user interface accessible through all devices. It is best to optimise the user experience by improving the website’s speed, loading time, and stability, along with user interactivity time with the website.
-
- Website architecture: Ensure that your website can easily navigate from one page to another with fewer clicks. Fix the broken internal and outbound Links for better performance. Also, find and fix the redirect chains and loops. Avoid too many redirects and ensure that the redirect leads to the final destination URL.
- Crawl errors: Identify crawl errors in your website through tools like Google Search Console or SEO crawlers. Broken links, server errors, and unlinked pages are some of the most common errors due to which search engine bots refrain from crawling & indexing your website.
- Optimised XML Sitemap: Ensure that your website has an optimised XML sitemap containing the right attributes and information about all the URLs for efficient crawling.
- Optimised robots.txt File: Instructions for search engines are contained in a robots.txt file. Using it, you may instruct search engines on how to crawl your website more effectively and stop them from crawling certain areas of your website.
Key Metrics for SEO in Technical writing:
SEO isn’t a one-time investment. We advise you to consider a few key performance indicators (KPIs) to understand how implementing SEO has impacted your website’s visibility.
- Crawl rate and Budget
- Keyword ranking
- Organic Traffic or session
- Page views
- CTR
- Bounce rate
- Average session duration
- Conversion rate
Common SEO tools:
There are both free and paid tools to monitor various vital metrics that we addressed in the above section. You can get started with these:
- Google Search Console: To get reports on your website’s presence and performance in Google SERP.
- Google Keyword Planner in Google Ads: For SEO keyword research.
- Google Analytics: To keep track of website visits, traffic, and demographics.
- SEMrush: To give you a comprehensive report on domain overview, traffic analytics, ranking against competitors, and other advanced tools.
- MozBar: To find the link metrics for any domains or Web pages like backlinks, domain authority, etc., you are competing against.
- Screaming Frog Tool: To identify and report various site errors like duplicate content, irrelevant meta tags, broken links, and more.
- Ahrefs: To analyse the website’s link profile, competitor analysis, and keyword rankings and optimise the SEO of the website accordingly.
You can use other available tools, but setting an objective comes first before venturing into SEO implementation in your technical pieces. Most of the results are evident in the long run, be patient and have clarity with your strategy. At most times, the goal is not to play the game well but to play better than your competitor.
We hope this blog answers some of the dwindling questions around SEO in technical writing. Good luck with your SEO journey!





