Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) is a secure electronic payment system that ensures the confidentiality and authentication of online transactions. It was developed to address the security concerns associated with online payments and provide a safe environment for conducting transactions over the Internet. SET works by encrypting sensitive financial information for all parties involved in the transaction. Let’s define secure electronic transactions in detail.
Table of Contents
What is Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)?
SET is a security protocol that enhances online payment security and integrity, especially those involving debit and credit cards. SET protects electronic payments by encrypting personal card details and authenticating users through digital certificates. SET ensures that only authorised parties can access sensitive information and that transactions are not tampered with.
SET was developed in the late 1990s by Visa and Mastercard, in collaboration with several technology and Internet companies, such as Microsoft, IBM, Verisign and Netscape. The aim was to create a standard and universal protocol for securing online payments and promoting the growth of e-commerce.
SET is not a payment system, but a security framework that can be linked with existing payment systems. It is founded on the principles of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). PKI relies on the use of both public and private keys to secure data through encryption and decryption, alongside digital certificates. This plays a crucial role in authenticating the parties engaged in the transaction.
SET uses four types of digital certificates:
-
Cardholder certificates
-
Merchant certificates
-
Payment gateway certificates
-
Authority certificates
These certificates are issued by trusted third parties and are used to establish a secure connection between the cardholder, the merchant, the payment gateway, and the card issuer.
Requirements for Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
- Mutual Authentication: It must verify both the customer (cardholder) and the merchant. This ensures that the customer is the rightful cardholder and the merchant is genuine.
- Data Confidentiality: Payment Information (PI) and Order Information (OI) should be encrypted to keep them safe from unauthorized access.
- Protection Against Tampering: The transmitted data should remain intact, with no changes allowed during the process.
- Interoperability and Security: SET should work smoothly across different systems while using strong security measures.
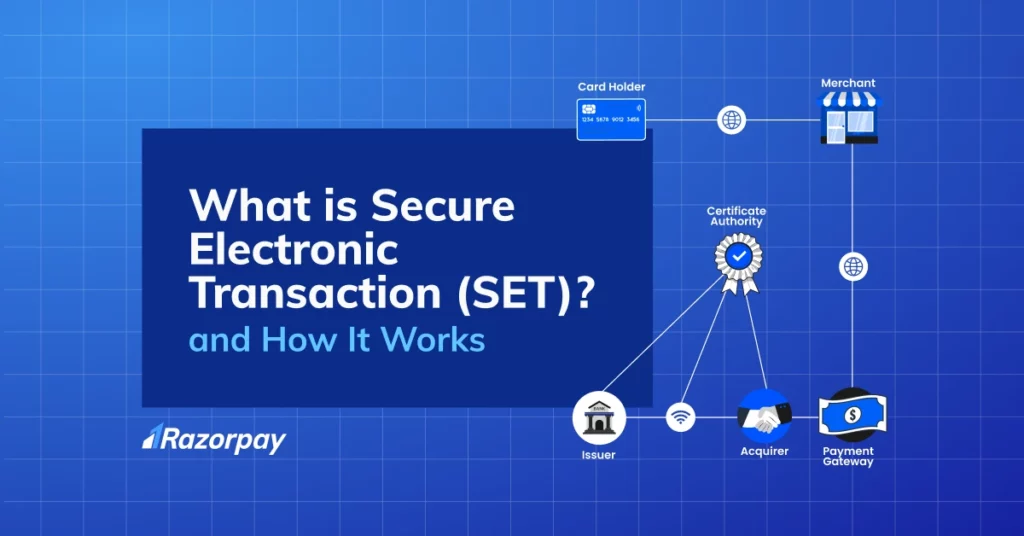
Secure Electronic Transaction: Key Participants Explained
1. Cardholder
A cardholder is an authorised user of a payment card, such as a MasterCard or Visa, issued by a financial institution. The cardholder can utilise the card to make purchases from merchants who accept the card as a form of payment. The cardholder is also the owner of the card account, which is used to track transactions and card balance.
2. Merchant
A merchant is an entity that sells goods or services to cardholders. To accept online payments, merchants must establish a relationship with an acquirer. This allows them to process payment transactions from customers securely.
Related Read: What Is a High-Risk Merchant Account? Factors to Determine High-Risk Merchant Account
3. Issuer
An issuer is a financial organisation, such as a bank, that provides payment cards to cardholders. Issuers are responsible for managing the debt incurred by the cardholder.
4. Acquirer
An acquirer is a financial organisation that collaborates with merchants to process payment authorisations and transactions. Acquirers facilitate electronic fund transfers to merchant accounts, enabling seamless online payments.
5. Payment Gateway
A payment gateway intermediates between SET and card payment networks. It facilitates communication between merchants and acquirers for payment authorisation, ensuring secure and efficient online transactions.
6. Certification Authority
A certification authority is a trusted entity providing public-key certificates to cardholders, payment gateways and merchants. These certificates ensure the security and authenticity of all the participants involved in the SET process.
Key Functionalities of Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
1. Provide Authentication:
To prevent fraud, SET allows customers to verify if a merchant has an existing relationship with a financial institution. This is done using standard X.509V3 certificates.
2. Customer/Cardholder Authentication:
SET ensures that only authorized users can use a credit card by verifying their identity with X.509V3 certificates.
3. Message Confidentiality:
This ensures that only the intended recipient can read the transmitted message. SET achieves this by using encryption techniques, with DES being a commonly used method.
4. Message Integrity:
SET prevents any unauthorized modifications to messages by using digital signatures. It secures messages with RSA digital signatures and SHA-1, while some cases also use HMAC with SHA-1.
How Does Secure Electronic Transaction Work?
Here is the step-by-step functioning of the secure electronic payment systems –
1. Customer Account Setup
You must open a credit card account with a bank supporting electronic payments and the SET protocol. You can visit the bank’s website or contact customer service to do so.
2. Certificate Issuance to Customer
Once your identity is verified, you will receive a digital certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This certificate contains essential details such as your name, public key, expiry date and certificate number. The CA ensures the authenticity and integrity of this certificate.
3. Merchant Certificate
To establish trustworthiness, merchants also obtain a digital certificate. This certificate verifies their identity and allows them to accept credit cards from certain issuers for secure electronic transactions.
4. Placing an Order
Browse through the merchant’s website and select the items you wish to buy. This creates a record of your order on the merchant’s site.
5. Merchant Verification
To assure authenticity, merchants send you their digital certificates, along with the order details. This helps you identify valid and authorised merchants.
6. Order and Payment Details
Next, you securely transmit your encrypted order and payment details to the merchant using your digital certificate for identification. The merchant cannot read this information but can verify your identity through your digital certificate.
7. Payment Authorisation Request
The merchant forwards the payment details to the payment gateway through an acquirer. They request payment authorisation from the payment gateway, which acts as an intermediary between the merchant and your credit card issuer.
8. Payment Gateway Authorisation
The payment gateway cross-verifies your credit card information with the issuer for authorising or rejecting the payment request. This verification process ensures online payment security by confirming that your credit card is valid and has sufficient funds.
9. Order Confirmation
Upon successful payment authorisation, the merchant confirms the order, providing payment authorisation details and purchase information.
10. Goods and Services Provision
Once the order is confirmed, the merchant provides the requested goods or services. This can include shipping physical products or granting access to digital content.
11. Payment Request by Merchant
Finally, after providing goods or services, the merchant requests payment from the payment gateway. The payment gateway interacts with various financial organisations, including the credit card issuer, acquirer and clearing house, to facilitate fund transfer from your account to the merchant’s account.
Security Architecture of Secure Electronic Transaction
1. SET Digital Certificates
Digital certificates are issued by trusted third parties called Certificate Authorities, which verify the identity and public key of the certificate holder.
Cardholder certificates are assigned to you by your card issuer, such as a bank or credit card company. These certificates contain your name, account number, expiration date, and public key. Cardholder certificates allow you to prove your identity and payment information to merchants and payment gateways, reducing the threat of fraud and identity theft.
2. SET Dual Signatures
Digital signatures are utilised for card authentication during transactions. Each transaction generates encrypted digital signatures for the merchant, customer and associated financial institutions. This secures the transaction by encrypting order information with the merchant’s public key and payment information with the acquiring bank’s public key.
3. SET Digital Wallet
SET activates your digital wallet through a password-based self-authentication process to enable secure payments. After authentication, your device sends the purchase and payment details to the merchant. Upon successful authentication, the issuing bank provides payment authorisation to the acquiring bank, hence informing the merchant of the success of the transaction.
What are the Benefits of Secure Electronic Transactions?
Some of the most popular advantages of Secure Electronic Transactions are:
1. Growing online sales:
With a projected growth of over 50% in global online retail sales in the next four years, it is essential to prioritise customer account security. Potential risks associated with fraud, data breaches and hacked accounts make it imperative for businesses to implement robust security measures.
2. Mitigating security risks:
The SET protocol was introduced as a solution to secure credit card transactions over networks. Its advanced encryption and algorithm systems are specifically designed to address security challenges associated with online payments. By leveraging SET, businesses can engage in secure payments, protect sensitive customer data and prevent unauthorised access.
3. Use of digital certificates:
SET issues digital certificates to users during transactions. These certificates are verified using digital signatures and certificates among all involved parties, including merchants, cardholders and financial entities. This ensures the authenticity and integrity of the transaction, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities.
4. Ensuring privacy and confidentiality:
The combination of digital signatures and certificates in the SET protocol ensures complete privacy and confidentiality for transactions. It safeguards sensitive information from unauthorised access or interception during transmission, instilling trust in customers while conducting online transactions.
Related Read: What is IVR Payment and How to Make IVR Payments?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an example of a secure electronic transaction?
Buying a book online and using your credit card to pay through a website with a padlock symbol in the address bar is an example of a secure electronic transaction. The padlock means your payment information is protected, thus making it safe to shop online.
2. Who developed the secure electronic transaction?
SET was developed by a consortium of companies, including Visa, Mastercard, and other major card issuers, in the late 1990s. The main purpose of SET was to secure electronic debit and credit card payments over the Internet by using encryption and digital certificates.
3. Why did SET fail to gain widespread adoption?
SET was complex, costly, and inconvenient for users and businesses. It required digital certificates, had high implementation costs, and was replaced by simpler alternatives like SSL/TLS and 3D Secure.
4. What is the weakness of secure electronic transactions?
SET provides enhanced security but can be vulnerable to data breaches or hacking. Cybercriminals may exploit system weaknesses to access sensitive data like credit card details. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential for protection of financial information.