Every product that crosses India’s border needs a unique identity, much like a passport. This identity is called the ITC HS Code, and it helps customs authorities, exporters, and importers classify goods in a consistent manner. While global trade follows a common 6-digit Harmonised System, India extends this framework to create a more detailed classification.
The ITC HS Code is an 8-digit Indian Trade Classification based on the Harmonised System. Using the correct code is mandatory when you file Shipping Bills for exports or Bills of Entry for imports in India. Customs systems do not accept filings without it.
More importantly, the ITC HS Code directly decides the customs duty, applicable GST rates, and your eligibility for export incentives or restrictions. Read on this guide to understand what the code means, how to find the right one, and how the full list is structured.
Key Takeaways
- The ITC HS Code acts as a standard product identifier for all imports and exports in India and is essential for customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
- India follows an 8-digit ITC HS structure, which builds on the global 6-digit Harmonised System to provide more precise product classification.
- The correct ITC HS Code directly impacts customs duty, GST rates, and eligibility for export incentives or restrictions.
- Understanding the structure of the ITC HS Code helps businesses identify the right classification on their own and reduces the risk of misclassification.
- Using official tools such as the DGFT website and ICEGATE ensures access to the updated ITC HS code list and supports accurate, compliant filings.
What Is an ITC HS Code?
An ITC HS Code is a standardised product classification system used in India to identify goods traded across borders. The code serves two purposes at the same time. First, it helps the government track trade volumes and values accurately across products and sectors. Second, it determines how your shipment gets treated at the border—covering customs duty, GST applicability, export incentives, and any restrictions or conditions.
In India, the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) maintains and updates this classification to align trade policy with global standards.
Understanding the Full Form: ITC-HS
- Indian Trade Clarification (ITC): India’s extended classification that adds product-level detail required for domestic trade policy and compliance.
- Harmonized System (HS): A globally accepted system for classifying traded goods in a uniform manner.
The ITC-HS is further divided: Schedule 1 applies to imports, while Schedule 2 applies to exports, helping you choose the correct code based on whether goods are entering or leaving India.
Related Read : Tariff and Non-Tariff Barriers in International Trade
Difference Between Global HS Code and Indian ITC HS Code
- Global HS Code
- 6 digits
- Maintained by the World Customs Organisation (WCO)
- Used by over 200 countries for international trade
- Indian ITC HS Code
- 8 digits
- Maintained by Indian authorities
- Builds on the global system for greater product clarity
The first six digits remain identical worldwide, ensuring global consistency. The last two digits are India-specific, allowing more precise classification for Indian customs, GST, and export-import regulations.
Explore Razorpay’s Global Payment Solutions
Structure of the 8-Digit ITC HS Code
The 8-digit ITC HS Code follows a clear, hierarchical logic. Each pair of digits adds a layer of detail, moving from a broad product group to a very specific item. This step-by-step structure mirrors how customs authorities assess goods at the border.
Once you understand how the code is built, you can often identify the correct classification yourself instead of relying blindly on third parties. This reduces errors, prevents delays, and helps you stay compliant during exports or imports.
Chapter (First 2 Digits)
The first two digits identify the broad industry or product family. For example, 09 covers Coffee, Tea, Mate and Spices. At this level, the focus is only on the general nature of the goods, not their form or quality.
Heading (Next 2 Digits)
The next two digits narrow the product type within the chapter. For instance, 0902 refers specifically to Tea, separating it from coffee or spices listed under the same chapter.
Sub-heading (Next 2 Digits)
These digits describe the product in more detail, often based on processing or form. For example, 090210 is used for Green Tea, distinguishing it from black or other varieties.
Tariff Item (Last 2 Digits)
The final two digits are India-specific. They classify precise variants used to determine duty rates, GST, or policy conditions, such as 10, 20, or 90 for different grades or pack types.
Why Are ITC HS Codes Important for Exporters?
The ITC HS Code is a compulsory detail in every export transaction. You must declare it in legal documents such as the Shipping Bill, and customs uses it to apply the correct duties, taxes, and policy rules to your goods.
If the code is wrong, exports can get delayed, incentives may be denied, and discrepancies may surface during audits. Using the correct ITC HS Code keeps your exports compliant and prevents avoidable disruptions.
Determining Customs Duty and GST
- Customs duty rates are directly linked to the ITC HS Code declared for your product.
- The code determines whether duty applies and at what rate.
- GST rates—5%, 18%, or 40%—are also mapped to HS-based classifications.
- An incorrect code can result in overpayment or short payment, both of which create compliance issues.
Claiming Export Incentives (RoDTEP / Drawback)
- Export schemes such as RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products) depend on correct product classification.
- Duty Drawback rates are also notified against specific HS codes.
- If you use an incorrect ITC HS Code, your export incentives claim may get rejected or reduced without notice.
Regulatory Compliance and Shipping Bills
- Every shipping bill must carry the correct ITC HS Code.
- The shipping bill forms the base for export records, incentives, and audit trails.
- Banks also rely on shipping bill data to issue Bank Realisation Certificates (BRC) or Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC), making accurate coding critical for closing the export cycle.
How to Find the Correct ITC HS Code?
Finding the right ITC HS code can feel overwhelming at first. India’s tariff schedule runs into thousands of entries, and many products sound similar on the surface. The good news is that you don’t have to guess. There are official, reliable tools that help you narrow down the correct classification easily.
Using the DGFT Website
The DGFT portal allows you to search the ITC (HS) classification directly from the official policy database.
1, Visit the official DGFT portal.
2, On the homepage, go to “Select your ITC(HS) Code / Product Selection”.
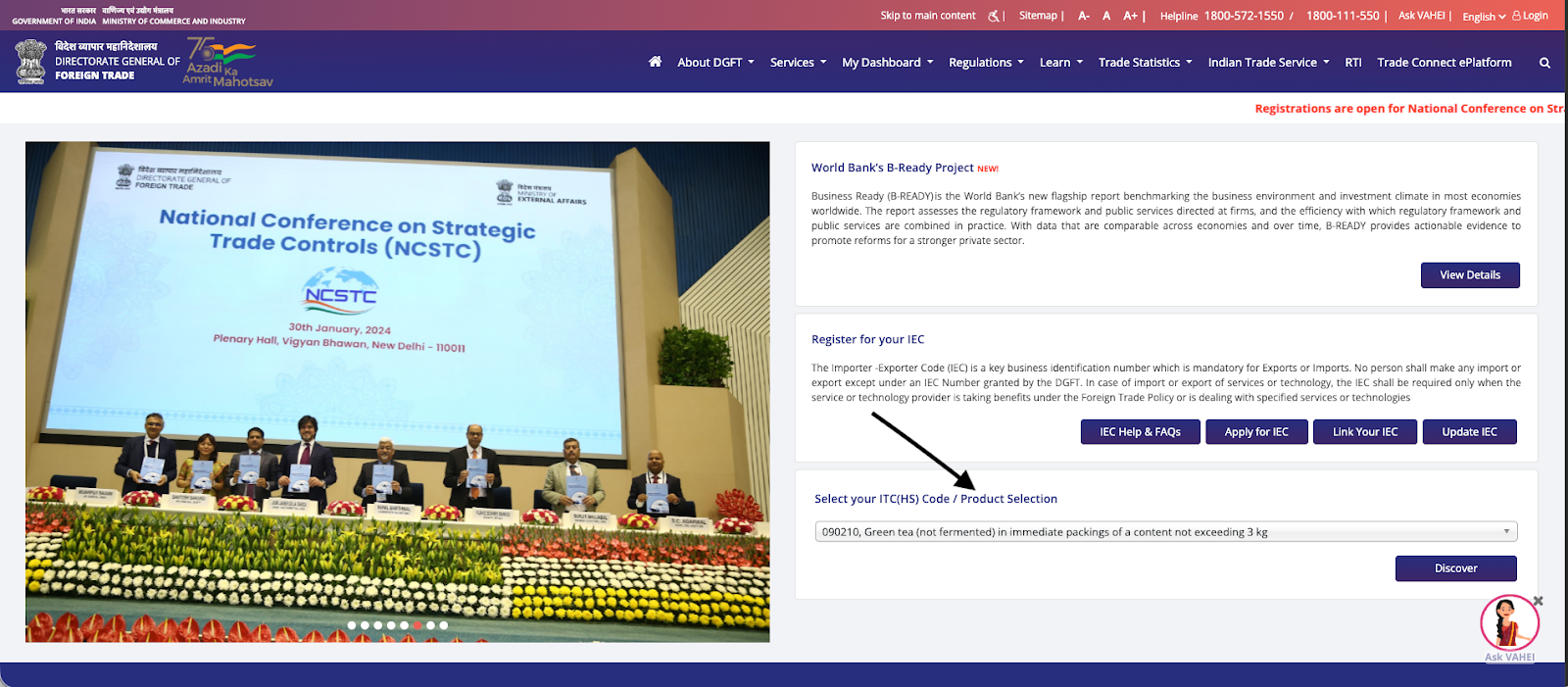
3, Search using relevant keywords or start with the applicable chapter number if you already know the broad product category.
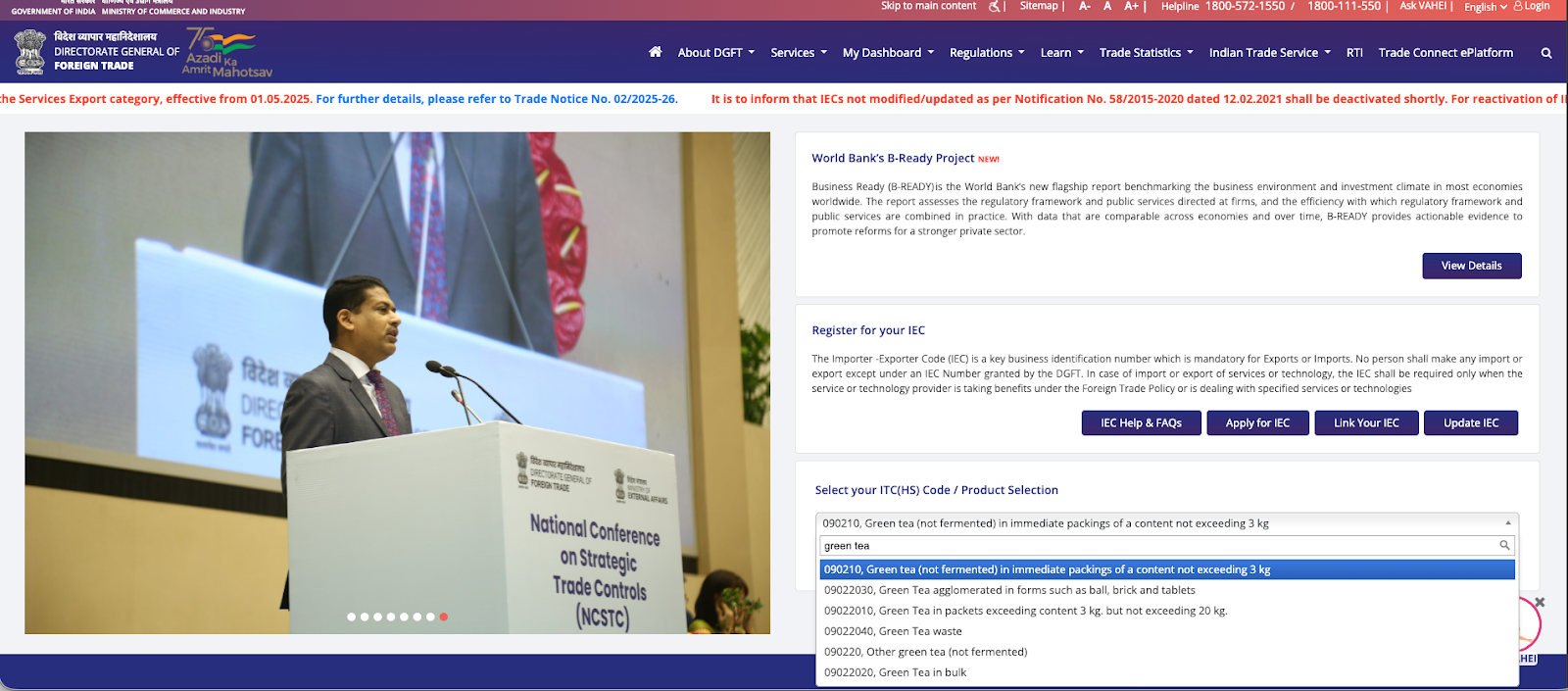
4, Review the detailed description carefully before finalising the ITC HS code.
Using the ICEGATE Portal
The ICEGATE portal helps you cross-check classifications from a customs processing point of view.
1, Visit the official ICEGATE website.
2, Click on Customer Support, then select Customs Duty Calculator.
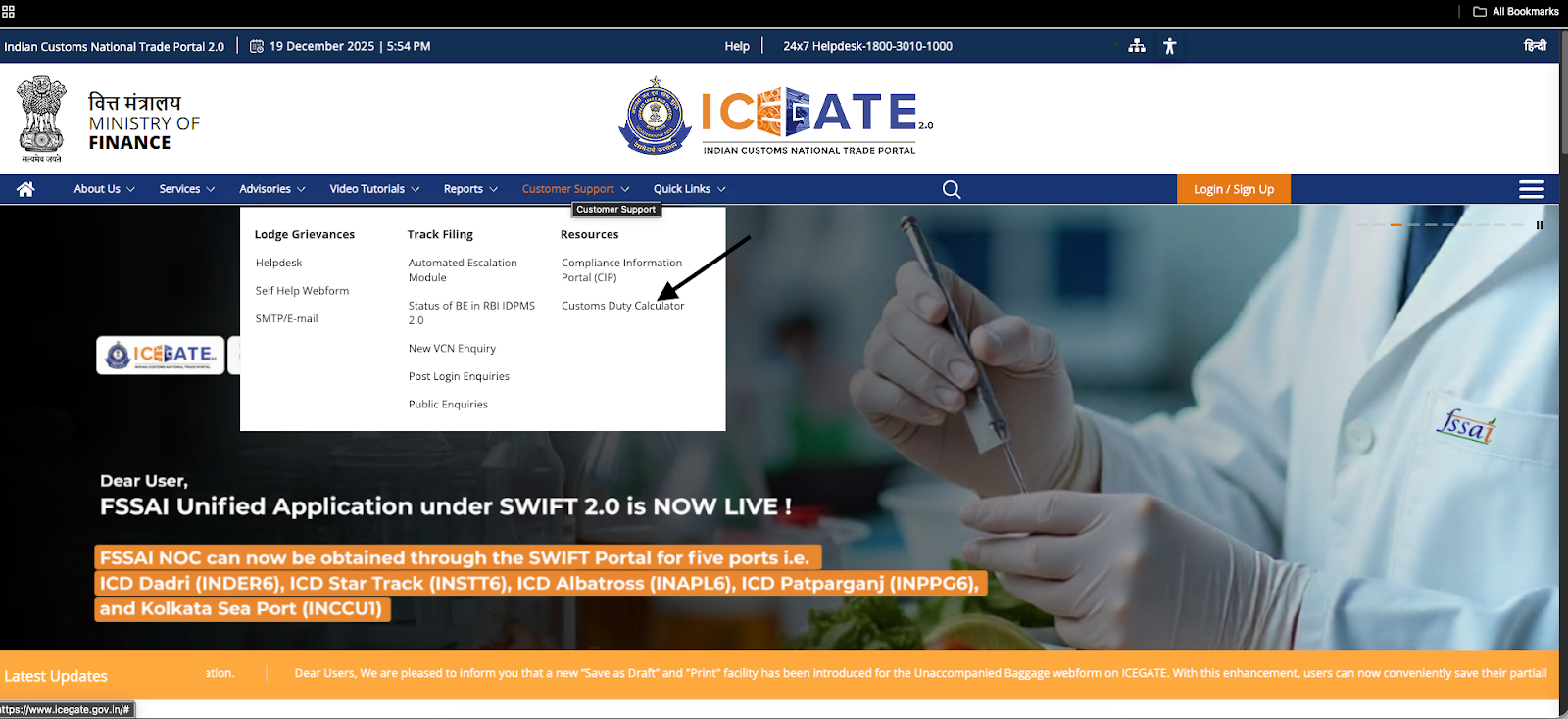
3, Open Trade Guide on Exports or Trade Guide on Imports, depending on your transaction.

4, Search using a clear product description or the chapter number if available.
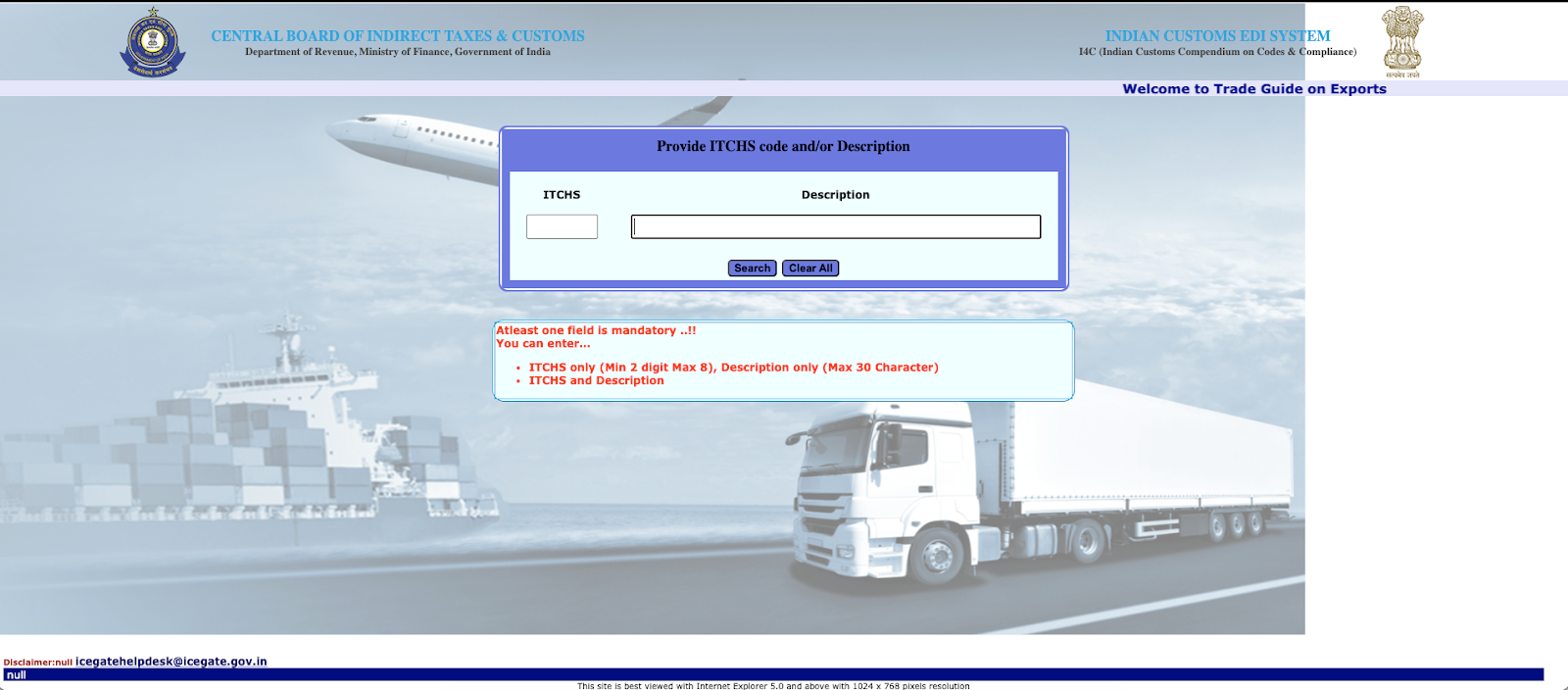
5, Review the HS codes suggested by the system.
6, Cross-check the full description to ensure it matches your product exactly.
Tips to Avoid Misclassification
- Do not rely only on the product name mentioned on invoices or marketing material. Always check the technical composition, primary use, and physical characteristics of the product, as classification depends on these factors.
- If your product is a combination of materials or serves multiple functions, refer to the General Rules for Interpretation (GRI). These rules explain how to classify mixed or composite goods when more than one heading seems applicable.
- For products with complex specifications or high-value shipments, it is safer to seek professional advice. A licensed Customs House Agent (CHA) can help confirm the correct ITC HS Code and reduce the risk of disputes, penalties, or clearance delays.
Overview of ITC HS Code List (Sections I–XXI)
The Indian ITC HS Code list is organised into 21 broad Sections, which together cover 98 Chapters. Each Section groups similar products, making it easier for you to narrow down the correct classification without scanning hundreds of individual entries. Once you identify the right Section, you can move to the relevant Chapter and then the exact 8-digit code.
ITC HS Code Sections at a Glance
| Section | Broad Coverage | Chapter Range |
| I | Live Animals & Animal Products | 1–5 |
| II | Vegetable Products | 6–14 |
| III | Animal or Vegetable Fats & Oils | 15 |
| IV | Prepared Foodstuffs, Beverages, Tobacco | 16–24 |
| V | Mineral Products | 25–27 |
| VI | Chemicals & Allied Industries | 28–38 |
| VII | Plastics & Rubber | 39–40 |
| VIII | Hides, Skins, Leather & Fur | 41–43 |
| IX | Wood, Cork & Articles | 44–46 |
| X | Pulp, Paper & Printed Materials | 47–49 |
| XI | Textiles & Textile Articles | 50–63 |
| XII | Footwear, Headgear & Umbrellas | 64–67 |
| XIII | Stone, Cement, Ceramics & Glass | 68–70 |
| XIV | Pearls, Precious Stones & Metals | 71 |
| XV | Base Metals & Articles | 72–83 |
| XVI | Machinery & Electrical Equipment | 84–85 |
| XVII | Vehicles, Aircraft & Vessels | 86–89 |
| XVIII | Precision Instruments & Clocks | 90–92 |
| XIX | Arms & Ammunition | 93 |
| XX | Miscellaneous Manufactured Articles | 94–96 |
| XXI | Works of Art & Special Provisions | 97–98 |
Common Challenges With ITC HS Codes
- Ambiguous Product Classification
Some products do not fit neatly into a single category. If your product has mixed materials or multiple uses, it may appear to qualify under more than one ITC HS Code. Choosing the wrong classification in such cases can lead to disputes with customs, delays in clearance, or reassessment of duties.
- Frequent Policy Updates and Amendments
The government revises ITC HS Codes from time to time to reflect changes in trade policy, tariffs, and international standards. These updates may add new codes, merge existing ones, or change descriptions. If you are not tracking these amendments, you may unknowingly use an incorrect code.
- Use of Outdated or Inactive Codes
Relying on old lists, spreadsheets, or past filings is a common mistake. Codes that were valid earlier may no longer be accepted by customs systems. Using an outdated ITC HS Code can result in filing errors, rejected Shipping Bills, or loss of export benefits.
Pro Tip: Before you finalise an ITC HS Code, always cross-check it on the latest DGFT ITC(HS) schedule rather than relying on past filings or third-party lists. If your product sits in a grey area, document the reasoning behind your classification and keep product specifications handy. This helps you justify the code during customs queries or audits and reduces the risk of future disputes.
Simplify Export Payments with Razorpay MoneySaver Export Account
Once you have classified your goods correctly using the ITC HS code, the next step is collecting export payments in a way that is fast, compliant, and easy to manage. This is where the Razorpay MoneySaver Export Account fits in, helping you receive international payments efficiently while keeping the process simple and compliant.
Here’s how it supports your export collections:
- You can accept international payments from customers across 180+ countries through local bank transfers and global cards, reducing friction for overseas clients while keeping collections smooth for you.
- Razorpay provides you with a virtual international account in your name, allowing your buyers to pay in foreign currencies such as USD, EUR, or GBP, which are then settled to your Indian bank account in INR.
- The account also supports modern payment methods like Apple Pay and Google Wallet, helping you cater to customers who prefer digital-first payment options.
- All international transactions, settlements, and payment statuses are managed within the Razorpay dashboard, giving you clear visibility and making reconciliation simpler.
- With transparent pricing and no forex markups, you know exactly what you will receive for each export transaction.
- Razorpay ensures RBI-compliant processing and provides automatic eFIRC for eligible export transactions, supporting smoother documentation and regulatory compliance.
Simplify Export Payments with Razorpay
Accept payments from 180+ countries via transfers, cards, Apple Pay
and Google Wallet with zero forex markup and auto eFIRC.
Conclusion
In Indian trade, the 8-digit ITC HS Code acts as the foundation for every import and export transaction. It defines how your goods are identified, taxed, and assessed for export benefits. Using the correct code helps you avoid legal disputes, prevents delays at customs, and ensures you receive the financial benefits you are entitled to.
To stay compliant, always verify your classification using official DGFT notifications and ICEGATE tools rather than outdated references. As the code list changes periodically, keeping track of updates is not optional. Regular checks help you stay aligned with current regulations and keep your cross-border trade smooth and predictable.
FAQs
1. What is the full form of ITC HS code?
ITC HS stands for Indian Trade Clarification based on the Harmonised System.
2. How does an ITC HS code differ from a standard HS code?
The global HS code, defined by the World Customs Organisation, uses 6 digits and is followed worldwide. India extends this by adding two additional digits, creating the 8-digit ITC HS code for more precise classification under Indian trade rules.
3. Where can I find the official ITC HS code list for India?
You can access the official and updated ITC HS code list on the DGFT website or through the ICEGATE portal, which is managed by Indian Customs.
4. Is the ITC HS code mandatory for GST invoices?
Yes. HS codes are mandatory on GST invoices. The number of digits required—4, 6, or 8—depends on your turnover and whether the transaction involves domestic supply or cross-border trade.
5. What happens if I use the wrong ITC HS code?
Using an incorrect code can cause customs delays, incorrect duty or GST payments, penalties, and rejection of export benefits or insurance claims.