Calculating income tax on employee salary is a complex process. If not done correctly, it can lead to errors and inaccurate tax filing at the year-end.
If you don’t know how to calculate income tax on salary, you have landed at the right place. This blog post will discuss the various aspects of income tax computation on employee salary with an example. Let’s dive right into it.
Table of Contents
Income tax slab for salaried individuals
During the Union Budget 2020, the central government announced a new tax regime for the taxpayers. The new tax regime has relatively lower slab rates than its predecessor, and it eradicates most of the deductions available in the previous version.
This year, the income tax rates remain unchanged for taxpayers. Nevertheless, employees can choose between the new tax regime and the old one. The table provided below shows a brief comparison between the two tax systems.
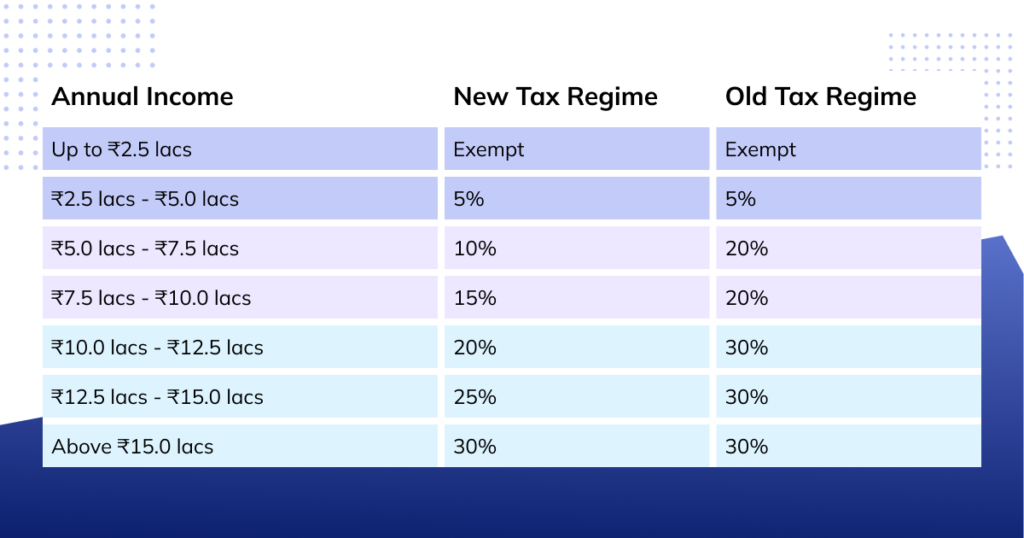 * Rs. 50,000 deduction is only available in the old regime
* Rs. 50,000 deduction is only available in the old regime
Tax Rebate u/s 87A of the Income Tax Act, 1961 is the lower of Rs. 12,500 or the actual tax payable. It is only applicable to individuals with taxable income up to Rs. 5 lacs per annum.
What is income from salary?
Income from salary is the compensation received by an employee for their services. However, this amount is considered income under the Income Tax Act only if there is an employer and employee relationship between the person who makes the payment and the person who receives the compensation. Typically, income from salary includes:
- Basic salary as per the terms of employment
- Allowance for meeting personal expenses
- Fees, commission, bonus, etc.
Various deductions to calculate income tax on salary
Here is a list of the various deductions considered under income tax laws to calculate income tax on salary.
1. House Rent Allowance (HRA)
Employees staying in rented accommodations can claim deductions for the same under the old tax regime. The income tax deductions are the least of the following:
- Total HRA paid
- Actual rent paid less than 10% of basic salary
- 50% of salary for metro cities or 40% of salary for non-metro cities
2. Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
Employees can claim LTA up to the amount of actual expense incurred (bills to be produced), twice in a block of four years. The LTA covers domestic travel only. Further, it doesn’t cover expenses incurred for personal reasons, such as leisure, food expenses, shopping, or entertainment.
3. Standard Deduction
In the interim budget of 2019, the total limit of standard deduction under income tax has been increased to Rs. 50,000.
4. Section 80C, 80CCD (1), and 80CCC
There are tax savings options wherein salaried employees can invest and claim an income tax deduction on salary up to Rs. 1.5 lacs. Some of the investments covered under the sections mentioned above include Employee Provident Fund (EPF), Life Insurance Premium, Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS), Pension schemes, etc. There are also many other government savings schemes included under these sections.
Read more in our blog post “Income Tax Deductions Under Section 80 For Individuals”
5. Deductions Against Loans
The principal and interest paid towards the home loan are eligible for deduction under section 80E subject to a maximum limit of Rs. 1.50 lacs. Employees can claim deductions for interest paid on home loans for up to Rs. 2.0 lacs under section 24.
How to calculate income tax on salary with example
Let us look at an example to understand the calculation of income tax on salary under both tax regimes.
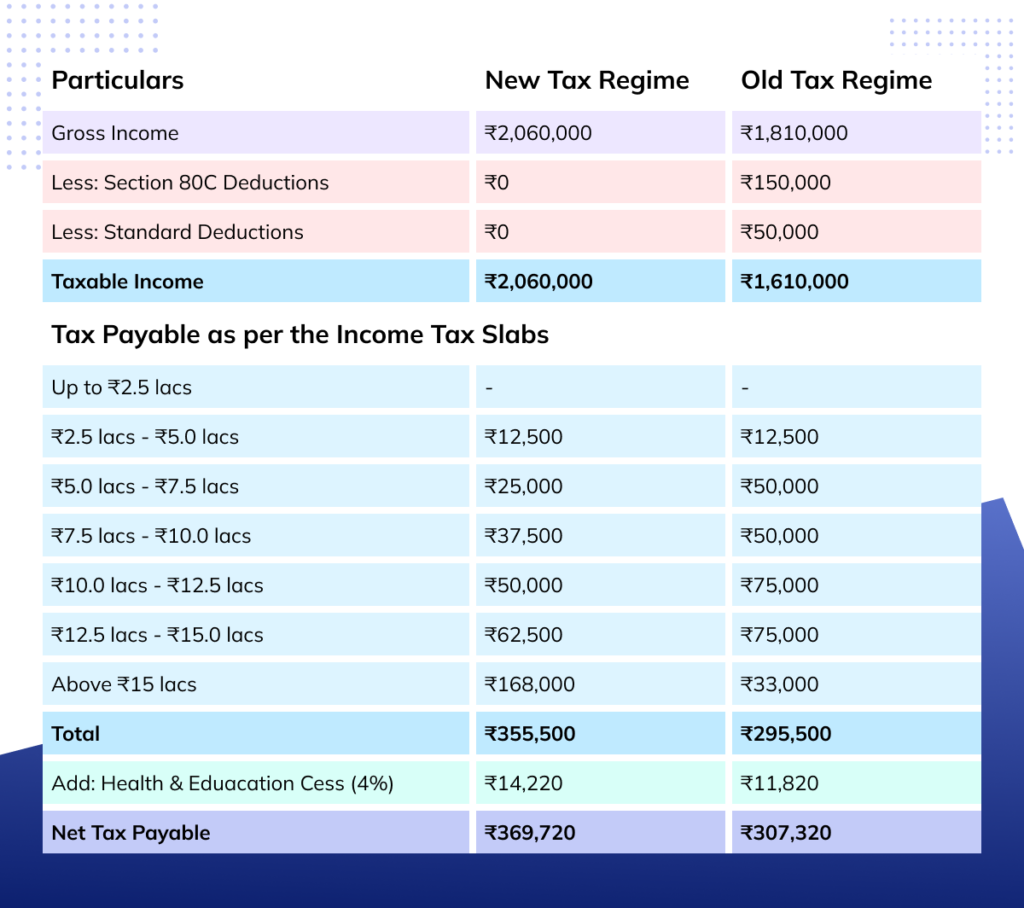
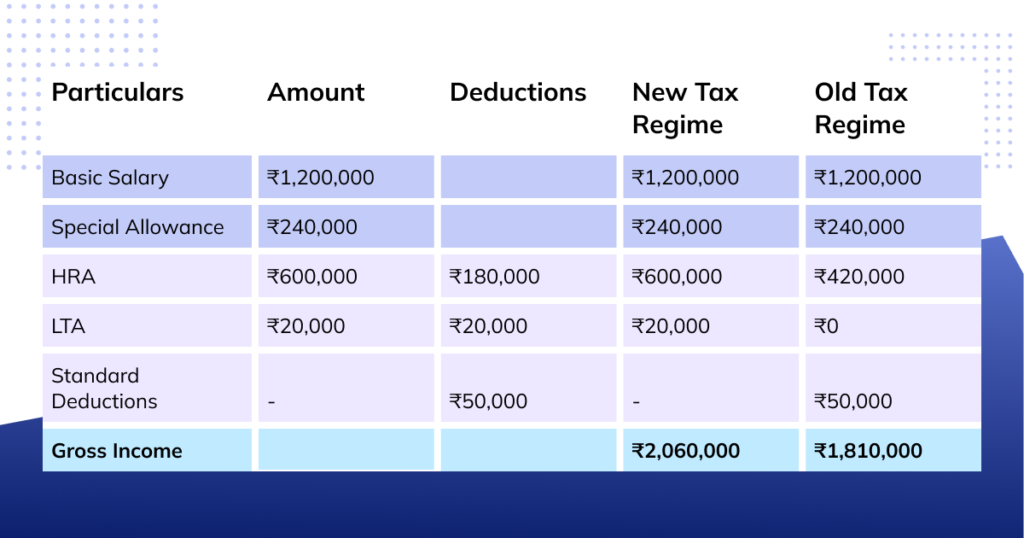
Rakesh, a 29-year-old, is working with ABC Technologies, earning Rs. 20.60 lacs per annum. He made investments under Section 80C of Rs. 1.5 lacs, claimed LTA of Rs. 20,000, and paid rent of Rs. 3,00,000 during the year. Let’s determine the payable tax amount under the new and old tax regimes.
 * Rs. 50,000 deduction is only available in the old regime
* Rs. 50,000 deduction is only available in the old regime
The HRA deduction is the least of
- Total HRA received, i.e., Rs. 600,000
- Actual rent paid less than 10% of basic salary, i.e. Rs. 300,000 – 10% × 1,200,000 = Rs. 180,000
- 40% of basic salary for non-metro cities, i.e. 40% × Rs. 1,20,000 = Rs. 480,000
So, the payable tax amount under the new tax regime will be Rs. 369,720 while that under the old tax regime will be Rs. 307,320 which is Rs. 62,400 lower than the new tax regime.
Calculate employee salaries with just a few clicks
Calculating employee salaries manually is cumbersome and extremely error-prone. Your HR team will have to spend hours every month to keep up with compliance and calculate salaries considering several factors. All these hours could be used to contribute to growing your business.
Say hello to RazorpayX Payroll, intuitive software that helps split employee salary into various components, such as HRA, Flexi benefits, etc. automatically. It also allows your employee to choose their preferred tax regime at the time of their investment declaration for the financial year. And does verifications of tax deductions at year-end.
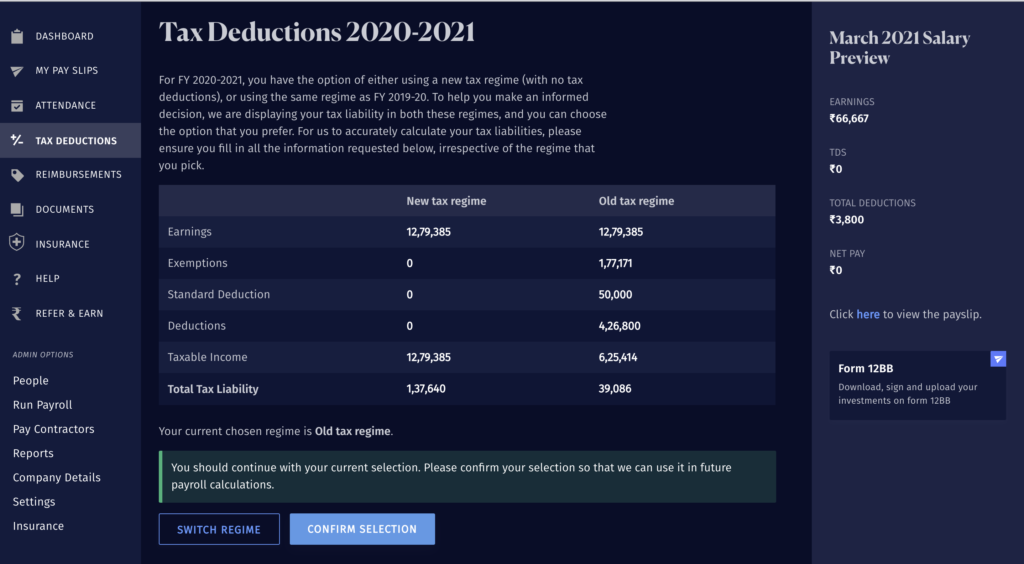 Not just that, employees can also see their projected taxes based on their income and regime so that they can make an informed decision.
Not just that, employees can also see their projected taxes based on their income and regime so that they can make an informed decision.
It will automatically compute the salary components and disburse them in the employee bank accounts based on the selected tax regime.
The entire payroll process takes just 3 clicks and less than 10 minutes.
Also, let’s not forget about the payroll compliances such as PF, PT, TDS, etc., that your HR and finance team has to compute and file every month. RazorpayX Payroll not only automatically calculates them but also files them for you, making the entire process fuss-free.
See why 2000+ leading Indian startups trust RazorpayX Payroll. We don’t even require your credit card details for the sign-up.
FAQs
What are different income heads under income tax?
Under the Income Tax Act, 1961, there are five income heads. 1. Income from salary 2. Income from capital gains 3. Income from house property 4. Income from profession 5. Income from other sources
What is income from other sources?
It includes income from various sources, such as interests, dividends, gifts, etc.